About EDNA - Efficient, Demand Flexible Networked Appliances
Over the past decade, EDNA has provided policy guidance aimed at improving the efficiency of smart devices and associated systems. In recent years EDNA has tackled the area of ‘demand flexible’ networked appliances.
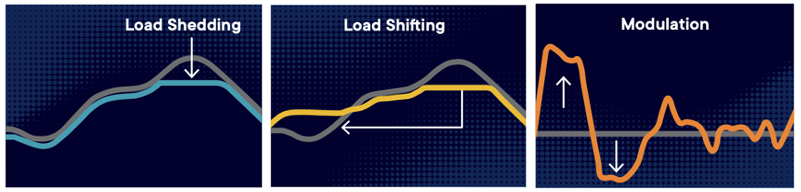
During its new term (2024 to 2029) EDNA will further increase its focus on demand flexible networked appliances. These appliances, empowering consumers, are able to react to requirements from the grid, for example to increase or decrease power consumption in response to renewable energy generation patterns, or to react to local demand constraints. Having such appliances installed is crucial to a net zero energy grid – their potential to reduce the requirement for expensive energy storage is substantial.
Though demand flexible networked appliances are increasing in importance, policy development is challenging as the topic is very new and no jurisdictions have yet enacted regulations. There are also challenges associated with ‘interoperability’ – ensuring that all kinds of networked appliances are ready to be externally controlled is complex. EDNA aims to guide its members through this new policy landscape.
To reflect the shift in focus, EDNA has changed its name to Efficient, Demand-Flexible Networked Appliances and the scope has become:
EDNA provides analysis and policy guidance to members and other governments aimed at improving the energy efficiency and demand flexibility of connected devices and networks.
As before, EDNA’s entry point to the topic remains at the device level. Collaborations with, and outputs from, other organisations remain heavily valued. EDNA will continue its current work on the energy efficiency of data centres, and as required over time, may choose to undertake further work on the energy efficiency of connected devices, as well as other related topics as they arise.